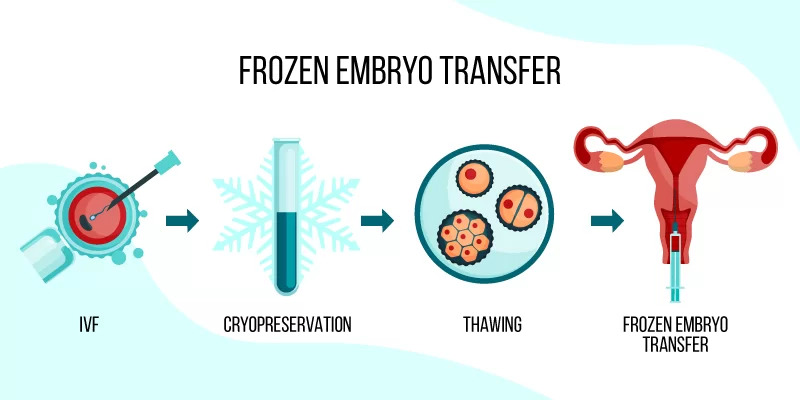
Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) is a fertility procedure in which a previously frozen embryo, created through in vitro fertilization (IVF), is thawed and transferred into the uterus of the intended parent or surrogate. This method allows individuals or couples to use embryos from a previous IVF cycle without undergoing another round of egg retrieval. FET is commonly chosen for medical, personal, or scheduling reasons and has become increasingly successful with advances in cryopreservation techniques, such as vitrification. It offers greater flexibility and often higher success rates compared to fresh transfers, especially when the uterine environment can be optimally prepared in advance.
Benefits of Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET)
- Higher success rates with improved embryo freezing techniques like vitrification
- Less physical strain compared to a full IVF cycle with egg retrieval
- Flexibility in timing for both patients and clinics
- Lower risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)
Considerations Before Choosing FET
- Uterine lining preparation is essential for successful implantation
- Embryo survival rate after thawing, though high, can vary
- Not all embryos may be viable after freezing and thawing
- Emotional and financial factors may influence the decision to pursue FET